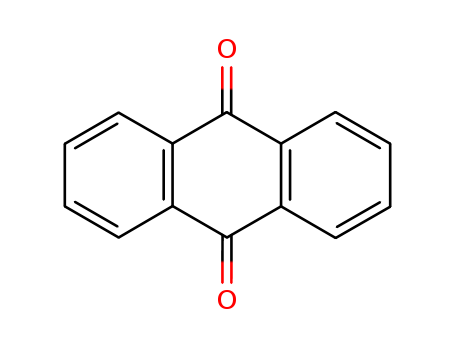
84-65-1
- Product Name:Anthraquinone
- Molecular Formula:C14H8O2
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:208.216
Product Details;
CasNo: 84-65-1
Molecular Formula: C14H8O2
Appearance: dull yellow powder
Factory Sells Anthraquinone, Buy High Grade 84-65-1 with Reasonable Price
- Molecular Formula:C14H8O2
- Molecular Weight:208.216
- Appearance/Colour:dull yellow powder
- Vapor Pressure:1 mm Hg ( 190 °C)
- Melting Point:284-286 °C(lit.)
- Refractive Index:1.659
- Boiling Point:377 °C at 760 mmHg
- Flash Point:141.4 °C
- PSA:34.14000
- Density:1.308 g/cm3
- LogP:2.46200
Anthraquinone(Cas 84-65-1) Usage
|
Chemical Properties |
Anthraquinone is a combustible, light yellow to green crystalline solid. Soluble in ethanol, ether and acetone, insoluble in water. It may be prepared by reacting benzene with phthalic anhydride. The compoundis the basis of a range ofdyestuffs. |
|
Occurrence |
Anthraquinones naturally occur in some plants (eg. aloe, senna, rhubarb, and Cascara buckthorn), fungi, lichens, and insects, where they serve as a basic skeleton for their pigments. Natural anthraquinone derivatives tend to have laxative effects. |
|
Uses |
Anthraquinone is used in paper industry as a catalyst to increase the pulp production yield and to improves the fiber strength through reduction reaction of cellulose to carboxylic acid. It is also used as a precursor for dye formation. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: Anthraquinone is an anthraquinone that is anthracene in which positions 9 and 10 have been oxidised to carbonyls. It is a colorless crystalline quinone used in producing dyestuffs such as alizarin. |
|
Synthesis Reference(s) |
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 102, p. 1457, 1980 DOI: 10.1021/ja00524a059The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 29, p. 987, 1964 DOI: 10.1021/jo01027a538Tetrahedron Letters, 24, p. 5499, 1983 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)94122-4 |
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Insoluble in water. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
Anthraquinone is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
|
Hazard |
Possible carcinogen. |
|
Fire Hazard |
Anthraquinone is combustible. |
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Nonflammable |
|
Agricultural Uses |
Repellent, Seed treatment: Used as a seed dressing or protectant. Banned in EU. |
|
Trade name |
(p)ANTHRAPEL?; FLIGHT CONTROL- PLUS?; HOELITE?; MORKIT?; REPELL? |
|
Safety Profile |
Moderately toxic by intraperitoneal route. A mild allergen. Mutation data reported. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame. To fight fire, use water, foam, CO2, water spray or mist, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes. |
|
Potential Exposure |
Anthraquinone is an important starting material for vat dye manufacture. Also used in making organics; and used as a bird repellent in seeds. |
|
Shipping |
UN3143 Dyes, solid, toxic, n.o.s. or Dye intermediates, solid, toxic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. |
|
Toxicity evaluation |
Anthraquinone is a stable compound that is virtually insoluble in water. It is not phytotoxic and does not inhibit germination of rice seeds or growth of sprouts. It has very low toxicity to birds and mammals, and it appears to be innocuous to insects as well. There is no known hazard to nontarget species from repellent applications of Flight Control. |
|
Incompatibilities |
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides |
|
Waste Disposal |
Dissolve or mix the material with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber. All federal, state, and local environmental regulations must be observed. |
84-65-1 Relevant articles
Alcohol oxidation and aldol condensation during base-catalyzed reaction of primary alcohols with 1-chloroanthraquinone
Shabany,Abel,Evans,McRobbie,Gokel
, p. 6705 - 6708 (2000)
When chloroanthraquinone is treated with...
Matrix Isolation of 3,4-Benzocyclodeca-3,7,9-triene-1,5-diyne
Koetting, Carsten,Sander, Wolfram,Kammermeier, Stefan,Herges, Rainer
, p. 799 - 803 (1998)
3,4-Benzocyclodeca-3,7,9-triene-1,5-diyn...
Self-immolative polymersomes for high-efficiency triggered release and programmed enzymatic reactions
Liu, Guhuan,Wang, Xiaorui,Hu, Jinming,Zhang, Guoying,Liu, Shiyong
, p. 7492 - 7497 (2014)
Stimuli-triggered disassembly of block c...
Quinaldinium Chlorochromate Supported on Alumina: A New and Efficient Reagent for the Oxidation of Alcohols
Degirmenbasi, Nebahat,Oezguen, Beytiye
, p. 1565 - 1569 (2003)
The new, mild chromium(VI) oxidizing age...
Degradable Holey Palladium Nanosheets with Highly Active 1D Nanoholes for Synergetic Phototherapy of Hypoxic Tumors
Gu, Kai,Huang, Zhijun,Li, Huawei,Li, Shanshan,Liu, Huiyu,Shi, Xinghua,Wang, Hui,Xu, Bolong
, p. 5649 - 5656 (2020)
Pd nanosheets (Pd NSs) have attracted ex...
Kinetics of amine catalysed oxidation of anthrone by oxygen in aprotic solvents
Serdyuk,Kasianchuk,Opeida
, p. 391 - 394 (2010)
Catalytic activity for the series of ali...
Photochemical Expulsion of Iodide from the 1-Iodoanthraquinone Radical Anion
Compton, Richard G.,Fisher, Adrian C.,Wellington, R. Geoffrey,Bethell, Donald,Lederer, Pavel
, p. 4749 - 4752 (1991)
The electochemical reduction of 1-iodoan...
Electrochemical oxidation-induced benzyl C–H carbonylation for the synthesis of aromatic α-diketones
Tan, Yu-Fang,Chen, Yuan,Li, Rui-Xue,Guan, Zhi,He, Yan-Hong
supporting information, (2021/12/21)
Electrochemical oxidation-induced direct...
g-C3N4/metal halide perovskite composites as photocatalysts for singlet oxygen generation processes for the preparation of various oxidized synthons
Corti, Marco,Chiara, Rossella,Romani, Lidia,Mannucci, Barbara,Malavasi, Lorenzo,Quadrelli, Paolo
, p. 2292 - 2298 (2021/04/12)
g-C3N4/metal halide perovskite composite...
84-65-1 Process route
-
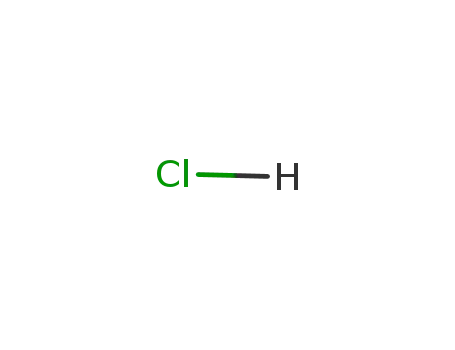
- 7647-01-0,15364-23-5
hydrogenchloride
-
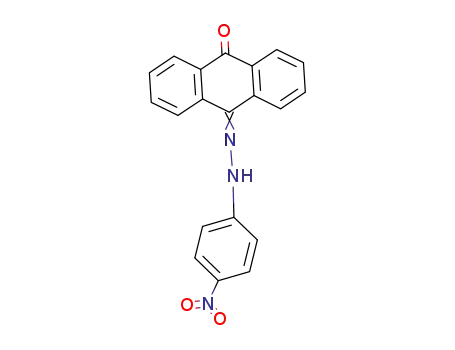
- 100151-74-4
anthraquinone-mono-(4-nitro-phenylhydrazone)

-
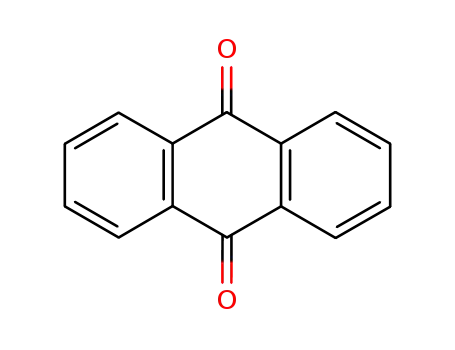
- 84-65-1
9,10-phenanthrenequinone

-
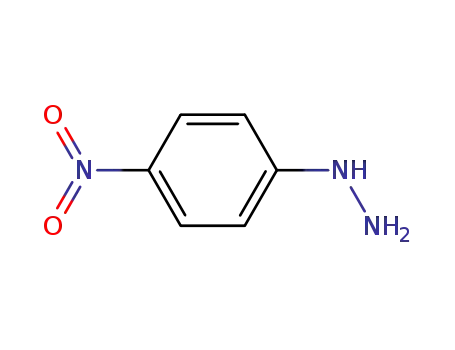
- 100-16-3
4-nitrophenylhydrazone
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
|
-
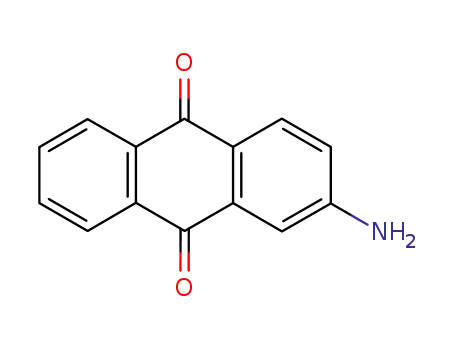
- 117-79-3
2-aminoanthraquinone

-
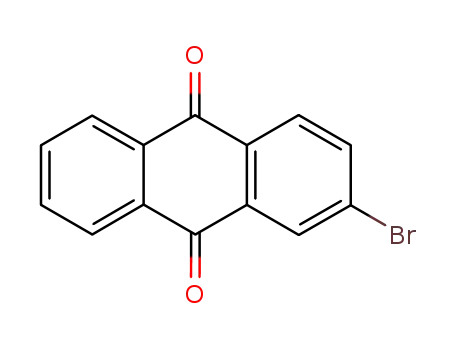
- 572-83-8
2-bromoanthracene-9,10-dione

-

- 84-65-1
9,10-phenanthrenequinone
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With tert.-butylnitrite; copper(ll) bromide; In tetrahydrofuran; acetonitrile; at 25 ℃; for 20h;
|
68% |
|
With tert.-butylnitrite; copper(ll) bromide; In tetrahydrofuran; acetonitrile; at 0 - 20 ℃; for 2h; Inert atmosphere;
|
37% |
84-65-1 Upstream products
-
71-23-8
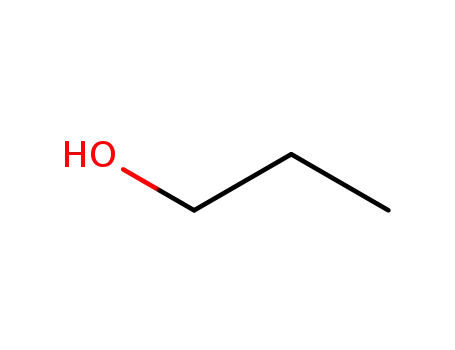
propan-1-ol
-
56-23-5
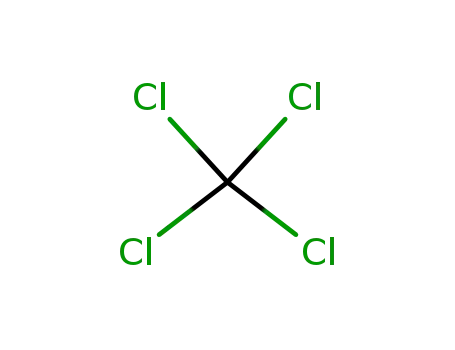
tetrachloromethane
-
17407-25-9
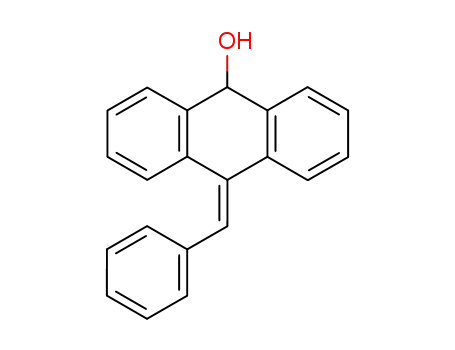
10-benzylidene-9,10-dihydro-[9]anthrol
-
79-21-0
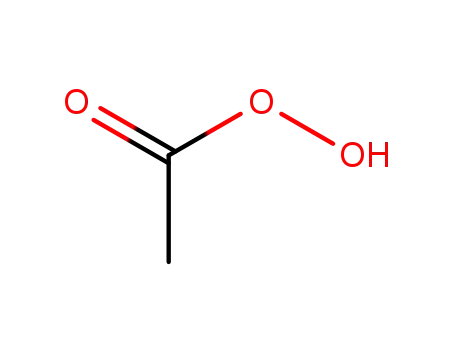
peracetic acid
84-65-1 Downstream products
-
133348-05-7
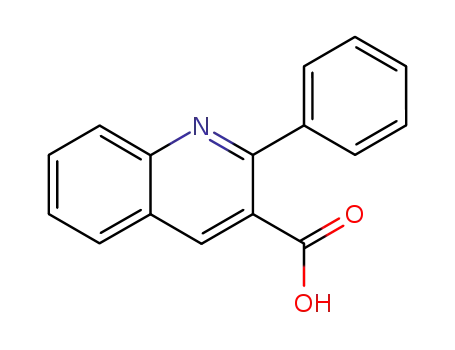
2-phenylquinoline-3-carboxylic acid
-
50971-40-9
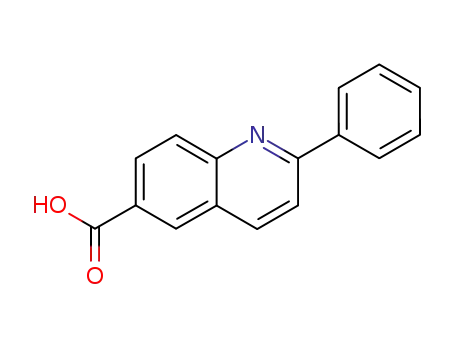
2-phenyl-quinoline-6-carboxylic acid
-
78787-97-0
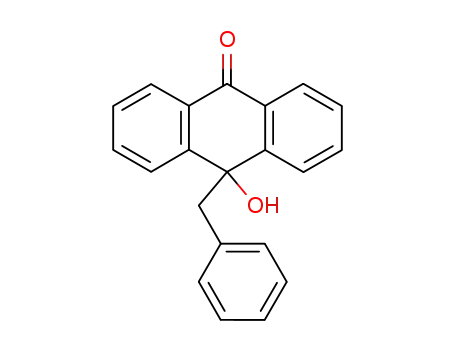
10-hydroxy-10-benzyl-9(10H)-anthracenone
-
6321-62-6
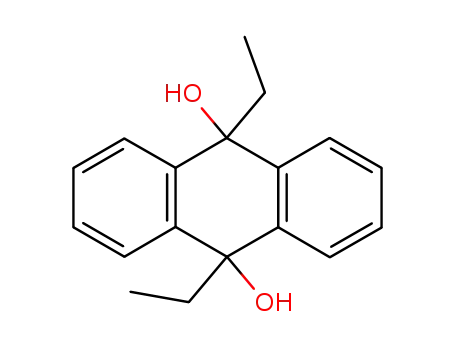
9,10-Diaethyl-9,10-dihydro-anthracen-9,10-diol
Relevant Products
-
1,2,3-Trifluoro-4-nitrobenzene
CAS:771-69-7
-
Norfloxacin
CAS:70458-96-7