100986-85-4
- Product Name:Levofloxacin
- Molecular Formula:C18H20FN3O4
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:361.373
Product Details;
CasNo: 100986-85-4
Molecular Formula: C18H20FN3O4
Appearance: Slight yellow powder
Buy High Quality Levofloxacin, Sale 100986-85-4 In Bulk Supply
- Molecular Formula:C18H20FN3O4
- Molecular Weight:361.373
- Appearance/Colour:Slight yellow powder
- Vapor Pressure:6.7E-14mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:218 °C
- Refractive Index:1.669
- Boiling Point:571.495 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:5.19±0.40(Predicted)
- Flash Point:299.43 °C
- PSA:75.01000
- Density:1.48 g/cm3
- LogP:1.54690
Levofloxacin hydrochloride(Cas 100986-85-4) Usage
|
Description |
Levofloxacin, the optically active S-isomer of the fluoroquinolone antibiotic ofloxacin, is two to four times more potent than ofloxacin with reportedly less side effects in treating infections of the lower respiratory and urinary tract, prostate infections and sexually transmitted diseases. It has broad and potent antibacterial activity over common Grampositive and -negative aerobic pathogens and obligate anaerobes. Different from the cephem antibiotics, levofloxacin is unique in its marked selectivity against members of the family Enterobacteriaceae and its negligible effect on predominant anaerobes. Levofloxacin also exhibits satisfactory antimicrobial effects in surgical infections and it may be used for treatment of gastrointestinal infections such as traveler’s diarrhea associated with the pathogenic Enterobacteriaceae. |
|
Chemical Properties |
Slight yellow powder |
|
Originator |
Daiichi (Japan) |
|
Uses |
Levofloxacin belongs to the class of medicines known as quinolone antibiotics. It works by killing bacteria or preventing their growth. Levofloxacin is active against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. It inhibits DNA gyrase (type II topoisomerase) and topoisomerase IV, thereby inhibiting cell division. |
|
Brand name |
Iquix (Sanofi Winthrop); Levaquin (Ortho-McNeil); Quixin (Sanofi Winthrop);Cravit. |
|
Therapeutic Function |
Antibacterial |
|
Pharmaceutical Applications |
For molecular weight and structure, see ofloxacin . Levofloxacin is the l-isomer of ofloxacin. |
|
Pharmacokinetics |
Oral absorption: >95% Cmax 500 mg oral: c. 5 mg/L after 1.5–2 h 750 mg oral: c. 8 mg/L after 1.5–2 h 500 mg intravenous (90-min infusion): c. 6 mg/L end infusion 750 mg intravenous (90-min infusion) :c. 12 mg/L end infusion Plasma half-life :6–8 h Volume of distribution:0.6–0.8 L/kg Plasma protein binding: <25%Co-administration with antacids, calcium, sucralfate and heavy metals decreases bioavailability and AUC. No interactions with warfarin or theophylline have been observed. Co-administration of a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug may increase the risk of convulsions. It undergoes limited metabolism and is primarily eliminated unchanged in urine by both glomerular filtration and tubular secretion. The free AUC:MIC ratio for Str. pneumoniae increases from about 55 to 70 when the daily dosage is raised from 500 mg to 750 mg.It is stable in plasma and does not revert to d-ofloxacin. It undergoes limited metabolism and is primarily eliminated unchanged in the urine. Renal clearance in excess of the glomerular filtration rate suggests that tubular secretion also occurs. Concomitant administration of either cimetidine or probenecid reduces renal clearance by approximately onethird. Clearance is reduced and half-life is prolonged in patients with impaired renal function (creatinine clearance <50 mL/min) requiring dosage adjustment in such patients. |
|
Side effects |
Side effects have been reported in 6–7% of patients and include fever, rash and other events common to the group. Elderly patients are at increased risk of developing severe tendon disorders including rupture, a risk increased by concomitant corticosteroid therapy. |
|
Metabolism |
Levofloxacin is metabolised to a very small extent, the metabolites being desmethyl-levofloxacin and levofloxacin N-oxide. These metabolites account for <5% of the dose and are excreted in urine. Excretion is primarily by the renal route |
InChI:InChI=1/C18H20FN3O4/c1-10-9-26-17-14-11(16(23)12(18(24)25)8-22(10)14)7-13(19)15(17)21-5-3-20(2)4-6-21/h7-8,10H,3-6,9H2,1-2H3,(H,24,25)/t10-/m0/s1
100986-85-4 Relevant articles
Experimental and computational study on the enantioseparation of four chiral fluoroquinolones by capillary electrophoresis with sulfated-β-cyclodextrin as chiral selector
Ma, Qianyun,Cong, Wei,Liu, Ye,Geng, Zikai,Lin, Ying,Wang, Zhaokun
, p. 549 - 557 (2021)
In this work, enantioseparation of four ...
GSH Induced Controlled Release of Levofloxacin from a Purpose-Built Prodrug: Luminescence Response for Probing the Drug Release in Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus
Pal, Suman,Ramu, Vadde,Taye, Nandaraj,Mogare, Devraj G.,Yeware, Amar M.,Sarkar, Dhiman,Reddy, D. Srinivasa,Chattopadhyay, Samit,Das, Amitava
, p. 2062 - 2070 (2016)
Fluoroquinolones are third-generation br...
Preparation of polar group derivative β-cyclodextrin bonded hydride silica chiral stationary phases and their chromatography separation performances
Zhao, Baojing,Li, Lan,Wang, Yuting,Zhou, Zhiming
, p. 643 - 649 (2019)
Three novel β-cyclodextrin compounds der...
Determination of levofloxacin in human urine with capillary electrophoresis and fluorescence detector
Tsai, Yu-Hsien,Bair, Ming-Jong,Hu, Cho-Chun
, p. 991 - 995 (2007)
In this study, we developed an analytica...
Enantioselective extraction of racemic ofloxacin by di(2-ethylhexyl) phosphoric acid and tartaric acid derivatives as mixed complex chiral selectors
Tian, Lingxing,Yang, Weijie,Chen, Xiaoqing,Xie, Yixi
, p. 642 - 645 (2011)
The distribution behavior of ofloaxcin (...
In-situ and one-step preparation of protein film in capillary column for open tubular capillary electrochromatography enantioseparation
Li, Ling,Xue, Xuqi,Zhang, Huige,Lv, Wenjuan,Qi, Shengda,Du, Hongying,Manyande, Anne,Chen, Hongli
, p. 2139 - 2142 (2021)
In this work, the phase-transitioned BSA...
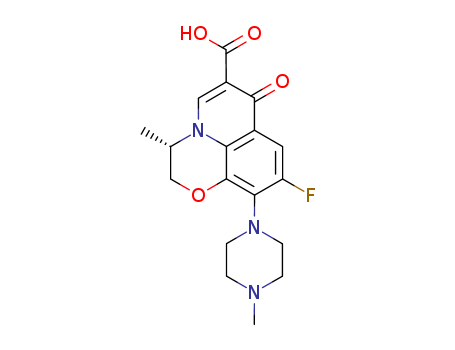
100986-85-4 Process route
-
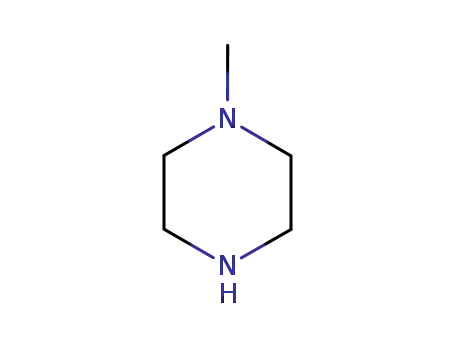
- 109-01-3
1-methyl-piperazine
-
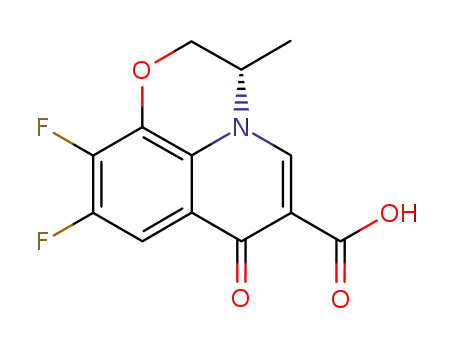
- 100986-89-8
levofloxacin Q-acid

-
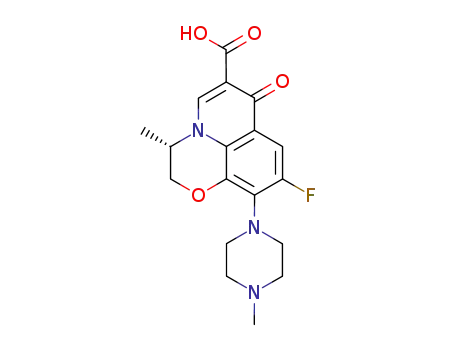
- 100986-85-4,83380-47-6
levofloxacin
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With potassium hydroxide; In water; at 55 ℃; for 24h; Reagent/catalyst; Time; Temperature; Solvent;
|
97.1% |
|
With nano iron oxide on ZrO2 coated sulfonic acid; In water; for 0.366667h; Reflux;
|
96% |
|
at 150 ℃; Microwave irradiation;
|
89% |
|
With pyridine; at 120 ℃; for 12h;
|
83% |
|
With BF3 etherate; triethylamine; In hydrogenchloride; methanol; diethyl ether; dimethyl sulfoxide;
|
55% |
|
In acetonitrile; Heating / reflux;
|
|
|
In dimethyl sulfoxide; isopropyl alcohol;
|
5.86 g (91.3%) |
|
In dimethyl sulfoxide; isopropyl alcohol;
|
106 g (92%) |
|
In dimethyl sulfoxide; isopropyl alcohol;
|
106 g (92%) |
|
In 2-methyl-propan-1-ol;
|
2.83 g (77.3%) |
|
In DMA (dimethyl acetamide);
|
11.48 g (89.3%) |
|
In butan-1-ol; at 120 - 125 ℃; for 6h;
|
|
|
With triethylamine; In dimethyl sulfoxide; at 90 ℃; for 8h;
|
|
|
In water; at 110 ℃; for 10.5h; Temperature; Green chemistry;
|
|
|
In water; at 120 ℃; for 15.5h; Temperature;
|
|
|
In water; at 110 ℃; for 10.5h; Temperature;
|
-
- 177472-30-9
C20H24FN3O4

-

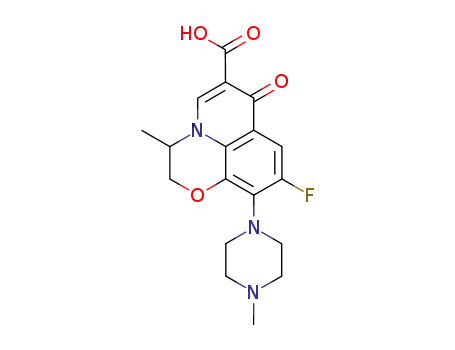
- 100986-85-4,83380-47-6
levofloxacin
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With hydrogenchloride; In ethanol; water; at 83 ℃; for 36h;
|
77.9% |
|
With hydrogenchloride; In ethanol; water; at 83 ℃; for 36h;
|
75.3% |
100986-85-4 Upstream products
-
109-01-3

1-methyl-piperazine
-
129306-33-8
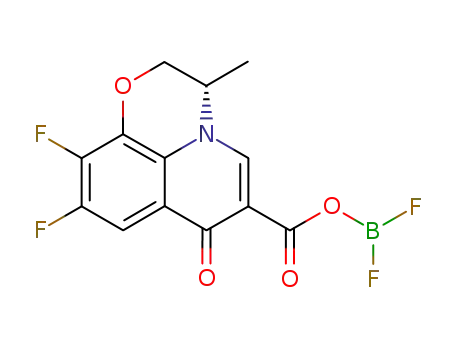
(-)-9,10-difluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-7-oxo-7H-pyrido<1,2,3-de><1,4>benzoxazine-6-carboxylic acid BF2-chelate
-
100986-89-8

levofloxacin Q-acid
-
82419-36-1
ofloxacin
100986-85-4 Downstream products
-
151250-76-9
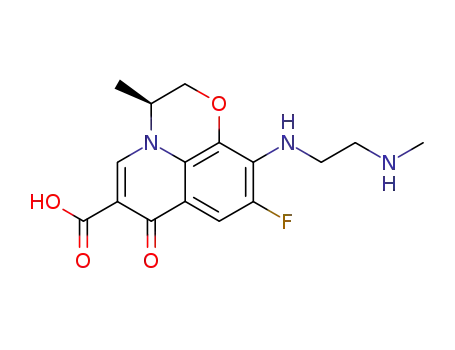
S-(-)-9-fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(1,4-diazapentyl)-7-oxo-7H-pyrido-<1,2,3-de><1,4>benzoxazine-6-carboxylic acid
-
117707-40-1
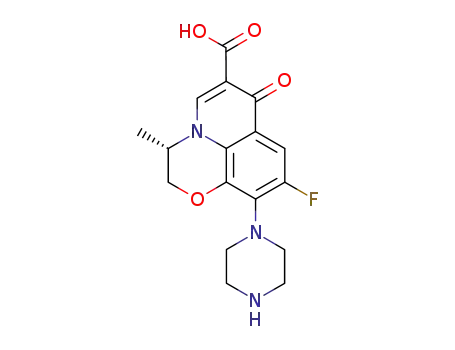
S-(-)-9-fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-7H-pyrido-<1,2,3-de><1,4>benzoxazine-6-carboxylic acid
-
151377-74-1
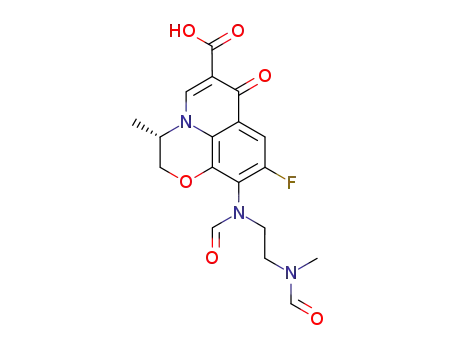
S-(-)-9-fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(1,4-diformyl-1,4-diazapentyl)-7-oxo-7H-pyrido-<1,2,3-de><1,4>benzoxazine-6-carboxylic acid
Relevant Products
-
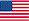
1,2,3-Trifluoro-4-nitrobenzene
CAS:771-69-7
-
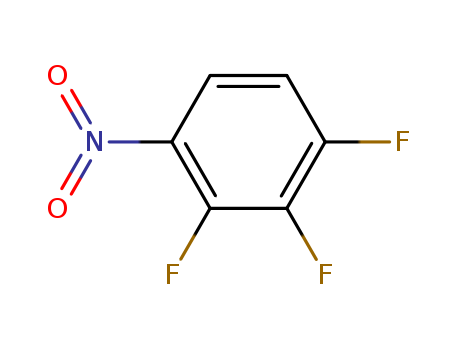
Sitagliptin free base
CAS:486460-32-6
-
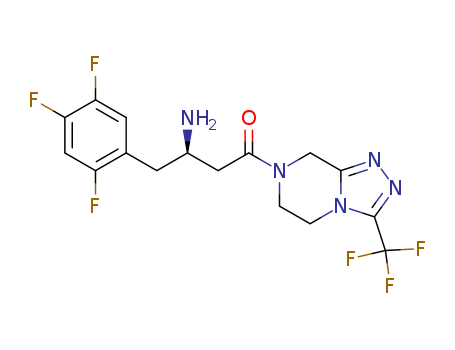
1-Nitroanthraquinone
CAS:82-34-8